Understanding Enterprise Switches: Core, Aggregation, and Access Layers
Enterprise networks typically follow a three-tier hierarchical model consisting of the core, aggregation (or distribution), and access layers. Each layer plays a distinct role in network operations, and the choice of switches at each layer can significantly impact network performance, scalability, and security.
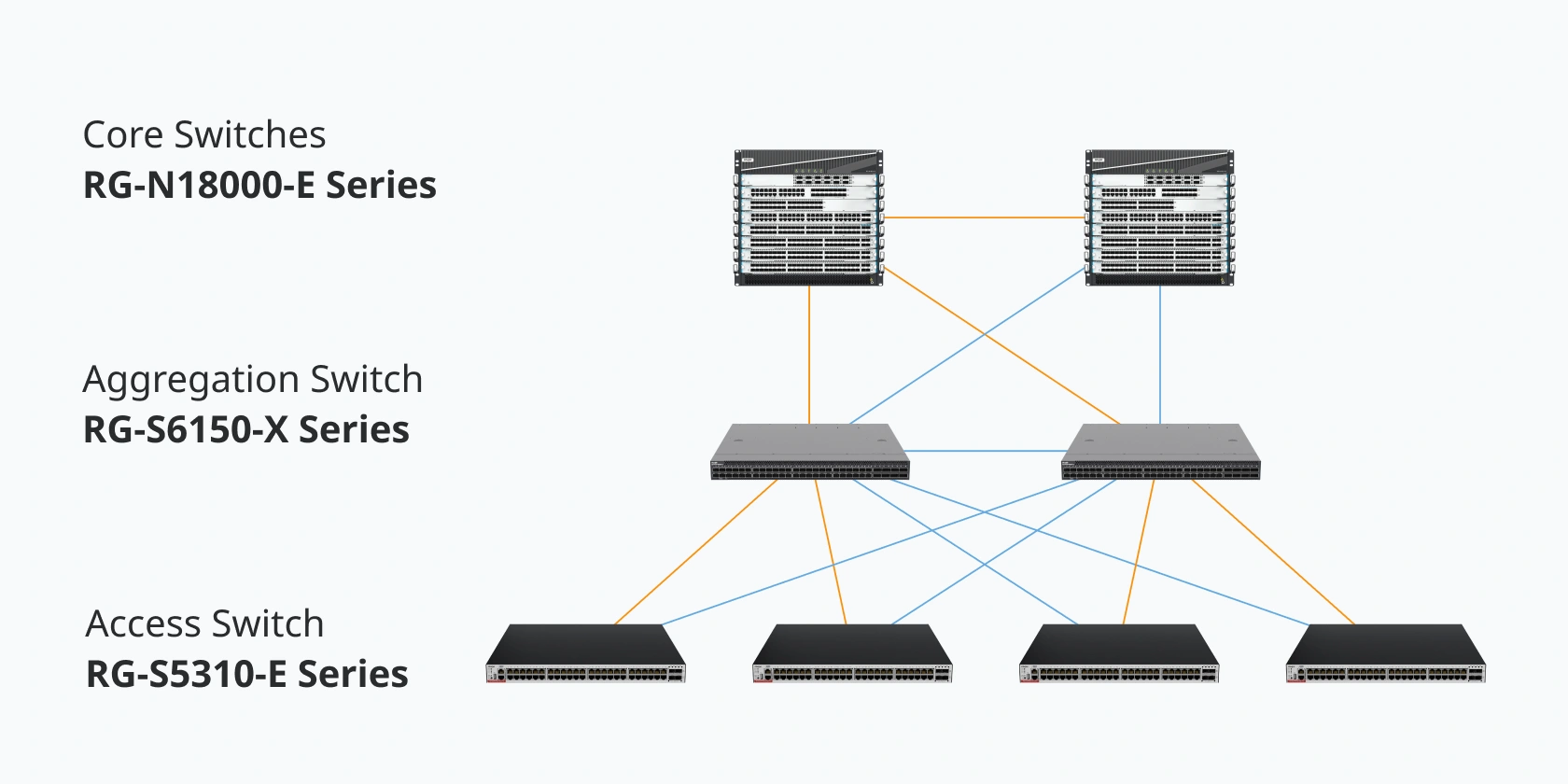
1. Core Switches: High-Performance Backbone
The core layer forms the backbone of an enterprise network, handling high-speed data transmission and ensuring network reliability through redundancy. These core switches deliver high throughput with scalable switching capacities, designed for performance-critical environments. They support advanced routing, virtualization, and strong fault-tolerance features, offering both modular and fixed options for flexible deployment across various enterprise network sizes.
2. Aggregation Switches: Intelligent Traffic Management
At the aggregation layer, switches manage traffic between the core and access layers. High-density port options and advanced redundancy protocols ensure continuous network availability. These switches excel in handling high-bandwidth traffic and support diverse deployment scenarios, from small businesses to large campus networks, with options that enable seamless network scaling as demand grows.
3. Access Switches: Efficient and Secure End-User Connectivity
Access switches connect end devices such as computers, IP phones, and wireless access points. They often include Power over Ethernet (PoE) functionality, making them ideal for connecting PoE-enabled devices. These switches support features like VLAN segmentation, ACLs, and user authentication protocols, ensuring secure and efficient connectivity at the network edge.
Overview of Core, Aggregation, and Access Layers in Enterprise Networks
Aspects | Core Layer | Aggregation Layer | Access Layer |
Functions | - High-speed data transmission and support high throughput - Redundancy and high availability - Rapid recovery and load balancing - High-density switches, support a large number of user connections | - Traffic aggregation and distribution - Connect different subnets - Apply network policies - QoS marking - Lateral expansion and redundancy | - Support a large number of connection devices - High port density - Security authentication - Network identity recognition - QoS support - High bandwidth, low latency switching equipment |
Hardware Requirements | - High bandwidth, low-latency switching equipment - Redundant links and hot standby - High reliability and fault tolerance | - High-speed switching equipment that supports traffic aggregation - Multiple switches and routers - Hot standby and redundant links | - High-density switches that support a large number of user connections - Support PoE, providing power supply - Security features and QoS support |
Security | - Boundary security, limiting external access - Protect the core network from unauthorized access | - Apply network policies and access controls - Isolate different departments and user groups - Prevent unauthorized access | - First point of entry, requiring high-level security - 802.1X authentication and port security - Prevent unauthorized device access |
Scalability | - Expand with higher-quality devices - Avoid CPU-intensive operations | - Support expansion in quality rather than quantity - High scalability | - Support a large number of connected devices, highly scalable - Simplify device addition and management - Expand the number of devices |
Management | - Simplify design, reduce failure points - Redundant design to minimize single points of failure - High availability and rapid recovery | - Distributed block management, issues in one part don't affect others - High availability and maintainability | - Device diversity leads to high management complexity - Requires maintenance of devices with numerous connections - Challenges in device management, troubleshooting, and implementing security policies |
Explore Ruijie’s Cutting-Edge Enterprise Switches for Every Network Layer

Key Considerations When Choosing Enterprise Switches and Network Switches
When selecting the right enterprise switches, it is essential to consider several factors, including network scale, performance needs, security requirements, and management capabilities. Here are some of the key factors to keep in mind:
1.Performance and Scalability
Enterprise switches must handle high traffic volumes while allowing for scalable growth. Core and aggregation switches are designed to provide high throughput and flexible expansion options, making them suitable for organizations of all sizes.
2.Security and Reliability
Network security is crucial in enterprise environments. Advanced security features, such as CPP/NFPP, DoS protection, and comprehensive access controls, protect against internal and external threats, ensuring that critical business data remains secure.
3.Ease of Management
Simplified management is key to efficient network operations. Cloud-based management platforms allow IT administrators to monitor, configure, and troubleshoot switches remotely, reducing the need for on-site maintenance and lowering operational costs. This is especially beneficial for businesses with distributed networks.
Ruijie’s Unique Advantages
Ruijie’s switch solutions offer several unique advantages that make them a standout choice for enterprise networks:
● Comprehensive Portfolio: Ruijie offers a wide range of switches that cover all layers of the enterprise network, from core to access, ensuring a seamless and integrated network infrastructure. In Q1 2024, Ruijie ranked first in market share for campus switches in China, according to an IDC report.
Q: How do Layer 2 and Layer 3 switches differ, and which is suitable for enterprise networks?
Q: What is Power over Ethernet (PoE) and how does it benefit enterprise networks?
Q: What are the benefits of using managed switches in an enterprise network?
Q: Is the ability to expand the network important for business growth, and why?
Featured blogs
- CXL 3.0: Solving New Memory Problems in Data Centres (Part 2)
- Ruijie RALB Technology: Revolutionizing Data Center Network Congestion with Advanced Load Balancing
- Multi-Tenant Isolation Technology in AIGC Networks—Data Security and Performance Stability
- Multi-dimensional Comparison and Analysis of AIGC Network Card Dual Uplink Technical Architecture
- A Brief Discussion on the Technical Advantages of the LPO Module in the AIGC Computing Power Network


















